Anyone in the LED industry knows the drill: a single P10 DIP module costs roughly the same as 1.5 ~2 time P10 SMD modules. Over the past few years, SMD technology has matured rapidly while staying affordable, so most LED display manufacturers have phased out DIP production to focus on SMD products.
But what exactly sets these two module types apart? If SMD is cheaper and more popular, why does DIP still have a place in some outdoor LED display applications? Today, we will guide you the difference between outdoor P10 DIP and SMD LED modules.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is an Outdoor P10 DIP LED Module?
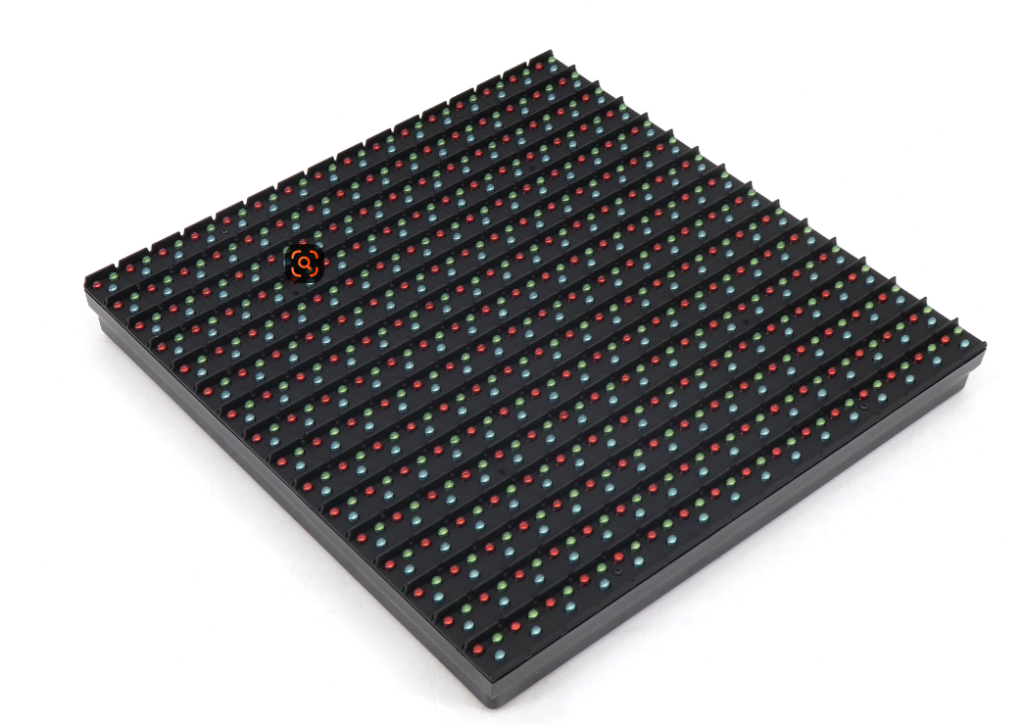
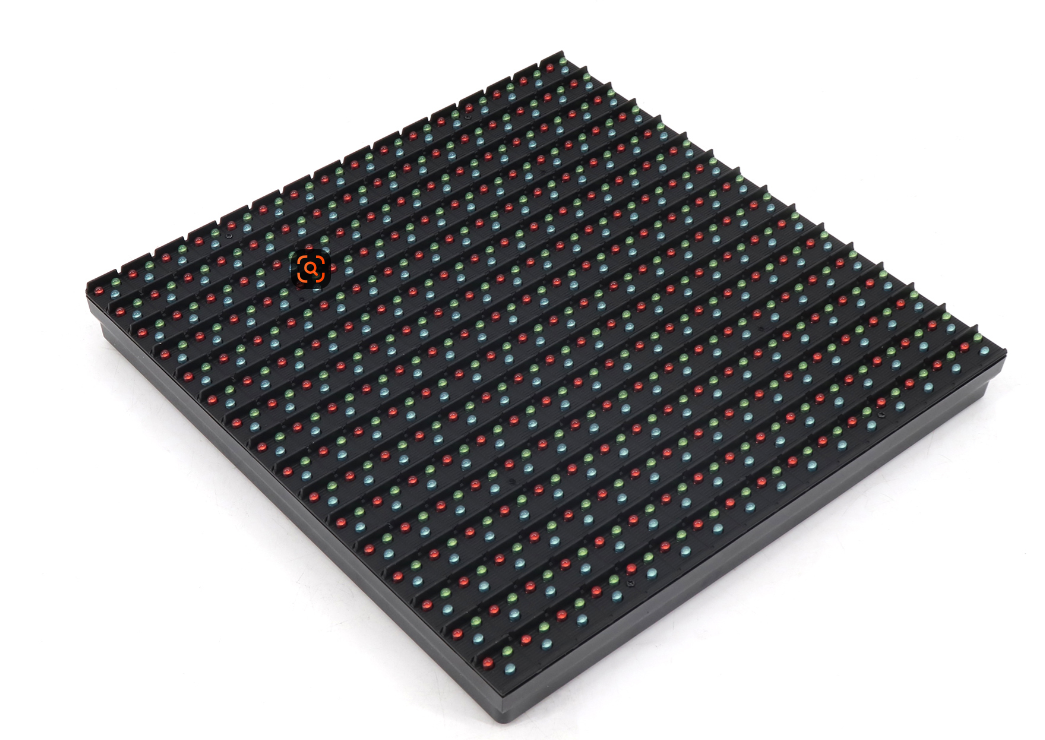
Outdoor P10 DIP LED modules have two key features:.
- 10mm pixel pitch: It is ideal for medium to long viewing distance.
- DIP lamp beads: It is cylindrical LEDs with metal pins that “dip” through holes in the PCB board.
These modules are a legacy technology but remain valued for outdoor use thanks to their inherent water resistance and omnidirectional light emission.
LED display Manufacturers encapsulate DIP lamp beads in durable epoxy, sealing the chips tightly to protect against moisture, dust, and physical impact. Common DIP lamp bead models include high brightness P10 and P16.
The PCB boards have hollow solder pads; workers or machines insert the lamp beads’ pins through these holes before soldering them in place.
| Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| Pixel Pitch | 10mm |
| LED Type | DIP346 / DIP346 3-in-1 (Red, Green, Blue discrete LEDs) |
| Pixel Configuration | 1R1G1B (three separate DIP LEDs) |
| Pixel Density | 10,000 pixels/m² |
| Module Resolution | 32 × 16 pixels / 32 × 32 pixels (varies by brand) |
| Module Size | 320 × 160 mm / 320 × 320 mm |
| Brightness | 6,000–10,000 nits (high brightness outdoor) |
| Viewing Angle | H: 110° / V: 60° (typical for DIP) |
| Best Viewing Distance | 10–80 meters |
| Refresh Rate | 960–3840Hz (depends on driver IC) |
| Grey Scale | 12–16 bits |
| Scan Mode | Static / 1/2 Scan (DIP commonly static) |
| Drive IC | ICN2038 / MBI5124 / Equivalent |
| Power Consumption (Avg.) | 300–400W/m² |
| Power Consumption (Max.) | 700–900W/m² |
| Cabinet Size | 960 × 960 mm / 960 × 960 mm (standard) |
| Cabinet Material | Iron / Aluminum |
| IP Rating | IP65 Front / IP54–IP65 Rear |
| Brightness Adjustment | 256–1024 levels automatic/manual |
| Working Temperature | -20°C to +60°C |
| Humidity | 10%–90% RH |
| Lifetime | ≥100,000 hours |
| Control System | Novastar / Colorlight / Linsn |
| Input Voltage | AC110V / AC220V |
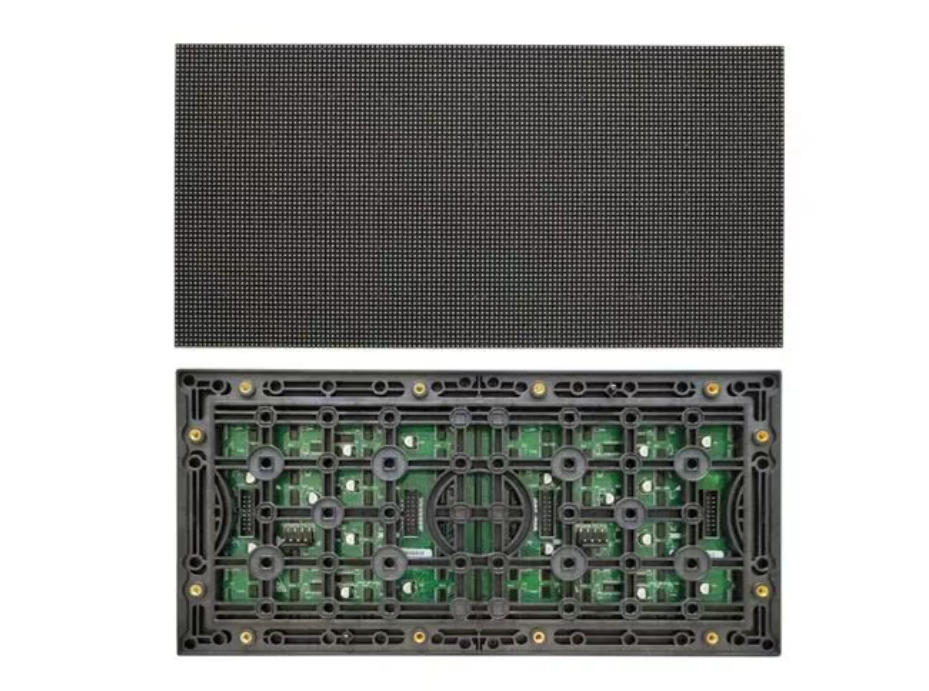
What Is an Outdoor P10 SMD LED Module?
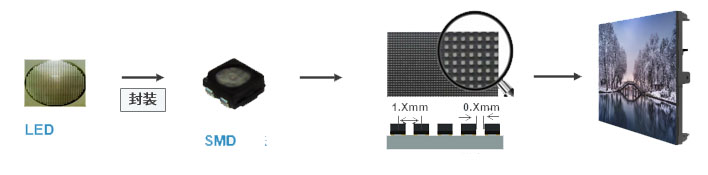
Outdoor P10 SMD LED modules use SMD lamp beads. It is square or rectangular LEDs that mount directly onto the surface of the PCB board, no pins required. SMD LED displays offer better uniformity and a sleeker profile than DIP.
The most common SMD lamp bead model for P10 outdoor modules is 3535. LED display Manufacturers encapsulate SMD beads in clear or diffused epoxy, and while they require additional waterproofing treatments for outdoor use. The advanced coating technologies have made them just as durable.
P10 SMD PCBs have flat solder pads. Te machines precisely place and solder the lamp beads.
| Item | Specification (Typical) |
|---|---|
| Pixel Pitch | 10mm |
| LED Type | SMD3535 / SMD2727 |
| Pixel Configuration | 3-in-1 RGB |
| Pixel Density | 10,000 pixels/m² |
| Module Resolution | 32 × 16 pixels / 32 × 32 pixels |
| Module Size | 320 × 160 mm / 320 × 320 mm |
| Brightness | 5,000–7,000 nits |
| Viewing Angle | H: 140° / V: 140° |
| Best Viewing Distance | 10–80 meters |
| Refresh Rate | 1920–3840Hz |
| Grey Scale | 14–16 bits |
| Scan Mode | 1/2, 1/4, or 1/8 scan (depends on model) |
| Drive IC | ICN2038 / ICN2153 / MBI5124 / MBI5153 |
| Power Consumption (Avg.) | 300–420W/m² |
| Power Consumption (Max.) | 750–980W/m² |
| Cabinet Size | 960 × 960 mm / 960 × 480 mm or customized |
| Cabinet Material | Iron / Aluminum |
| IP Rating | IP65 Front / IP54–IP65 Rear |
| Brightness Adjustment | Automatic / Manual 256–1024 levels |
| Working Temperature | -20°C to +60°C |
| Humidity | 10%–90% RH |
| Lifetime | ≥100,000 hours |
| Control System | Novastar / Colorlight / Linsn |
| Input Voltage | AC110V / AC220V |
Core Differences Between Outdoor P10 DIP and SMD Modules
The difference between DIP and SMD modules are four key areas: lamp bead design, PCB board structure, production processes, and ultimately, cost and performance. Let’s break these down one by one.
Lamp Bead & PCB Board Differences
Lamp bead design is the most obvious distinction. SMD lamp beads,like the 3535 model are small, flat, and square or rectangular. LED Manufacturers place the LED chips inside metal frames before filling them with epoxy and curing it, resulting in a low-profile, front-only light-emitting design.
The SMD modules PCB boards have dedicated flat solder pads on one side; the lamp beads attach directly to these pads, creating a smooth, even surface that contributes to uniform display quality.
However, DIP lamp beads are cylindrical with two metal pins protruding from the bottom. Their epoxy encapsulation has been refined over decades, making them naturally waterproof and capable of emitting light in all directions.
DIP PCB boards have hollow solder pads. The lamp beads’ pins pass through these holes, and the beads sit raised above the board surface after soldering.
Production Process Differences
SMD relies on full automation, while DIP requires a mix of machine and manual work, making it slower and more labor-intensive.
SMD module production is a streamlined, fully automated process:
First, machines print solder paste onto the IC side of the PCB board.
Next, they place ICs, simple header connectors, and power sockets onto the paste. The board then goes through a reflow oven, where the solder paste melts and hardens to fix the components in place.
After that, machines print solder paste onto the lamp bead side of the board, place the SMD LED beads precisely onto the pads, and send the board through the reflow oven again.
The final steps include testing, aging, and minor touch-ups. They are highly efficient thanks to automation.
DIP module production is more cumbersome, blending machine and manual work. The process starts similarly:
Printing solder paste on the IC side, placing ICs, and passing through a reflow oven. But here’s where it diverges: Workers must manually insert each DIP lamp bead into the PCB’s hollow pads one by one.
After insertion, the board undergoes a wave soldering process to secure the lamp beads’ pins. Then, workers manually solder the power sockets and header connectors .
Finally, the modules go through testing and aging. This mix of manual labor slows down production, increases labor costs, and raises the risk of human error.
Advantage Comparison: P10 DIP vs. SMD
When it comes to performance, DIP and SMD modules each have distinct strengths. Let’s compare them across three critical outdoor display metrics: brightness, display quality, and lifespan.
Brightness:
DIP modules have better brightness, making them more visible in direct sunlight. Most P10 DIP modules reach 6,000–8,000 nits, while standard P10 SMD modules range from 5,000–7,000 nits.
This gap exists because DIP’s omnidirectional light emission spreads more broadly, and the larger chip size in DIP beads. For outdoor applications with extreme sunlight , DIP’s extra brightness ensures content remains readable. That said, high-brightness 8,000 nits+ SMD models have narrowed this gap. Therefore, SMD is a viable option for most outdoor scenarios.
Display Quality
SMD modules dominate when it comes to display uniformity and image smoothness. Their flat, surface-mounted lamp beads sit evenly on the PCB, emitting light in a consistent, front-facing direction.
It creates sharp, smooth images with no “hot spots” or uneven brightness. Hoewever, DIP modules have raised, cylindrical beads that emit light omnidirectionally. The uneven surface and scattered light result in less uniform images. You might notice slight brightness variations or a “grainy” look, especially up close. For image quality application, SMD is the clear choice. DIP works better for text-based displays.
Lifespan:
DIP modules generally have a longer lifespan than SMD. It is about 80,000–100,000 hours, while 60,000–80,000 hours for SMD. This is due to two factors: larger LED chips can handle heat better and degrade more slowly and more robust encapsulation.
DIP’s epoxy encapsulation fully seals the chip, protecting it from moisture, dust, and thermal stress. For SMD beads, while well-encapsulated, use smaller chips and require additional waterproofing layers ,like conformal coating) for outdoor use. Over time, these layers can degrade, slightly reducing lifespan. For long-term outdoor installations , DIP’s longer lifespan justifies its higher cost; for shorter-term projects or those with regular maintenance, SMD’s lower cost makes it more practical.
Use Case Comparison: Where Each Module Excels

You should consider project’s needs: brightness requirements, display content, environment, and budget.
SMD Modules:
SMD’s versatility is its biggest asset. It works equally well in indoor and outdoor environments. Outdoor applications include shopping mall billboards, building facade displays, and outdoor event screens . Indoor uses range from conference room displays and school notice boards to hospital information screens and retail digital signage.
SMD’s uniform display quality makes it ideal for video content, while its lower cost suits large-scale installations. Even in outdoor settings, advanced IP65 rated waterproofing ensures SMD modules hold up to rain, dust, and temperature fluctuations.
DIP Modules:
DIP modules are now mostly limited to specialized outdoor applications . The top use case is traffic control displays,like road signs, pedestrian signals, and highway information boards). These require 24/7 operation in all weather conditions and need to be visible in direct sunlight. Other uses include outdoor industrial displays and remote outdoor billboards. DIP’s omnidirectional light emission also makes it suitable for displays viewed from wide angles, though SMD’s wider viewing angles have narrowed this advantage.
Why the Price Gap? DIP vs. SMD Cost
The biggest reason DIP modules cost nearly 1.5~2 time as much as SMD due to production efficiency and material costs.
Lamp bead costs:
DIP lamp beads are more expensive to produce than SMD. They use larger LED chips and thicker epoxy encapsulation, more raw materials and more complex molding. SMD beads use smaller chips and simpler square/rectangular encapsulation, with no pins.
Labor costs:
DIP production relies heavily on manual work, which is time-consuming and expensive. Inserting lamp beads one by one, manual soldering of power sockets/connectors, and additional quality checks to fix misaligned beads, add significant labor hours. SMD production is fully automated. The machines handle placement, soldering, and testing at a fraction of the time and cost. A single SMD production line can produce 1,000+ modules per day, while a DIP line might only produce 300–500 modules in the same time.
Additional processing costs:
While DIP has inherent water resistance, it still requires extra steps like epoxy coating for the PCB and connector sealing. SMD modules need conformal coating or waterproof enclosures for outdoor use, but these are automated processes that add less cost than DIP’s manual waterproofing steps.
Economies of scale:
Most LED manufacturers now focus on SMD, so SMD production volumes are higher, driving down material and production costs further. DIP’s declining production volumes mean manufacturers can’t leverage the same economies of scale, keeping prices high.
Outdoor P10 DIP vs. SMD Module Price
As of 2025, the price difference between outdoor P10 DIP and SMD modules remains significant, with DIP costing roughly 70–100% more than SMD.
Outdoor P10 SMD modules ,like 3535 beads, 5,000–7,000 nits, IP65 waterproof. It ranges from $15–$25 per module. High-brightness 8,000 nits+ models cost slightly more. It is about $20–$30 per module. The exact price depends on the manufacturer, lamp bead quality , and additional features . For large orders (500+ modules), LED display suppliers often offer discounts, bringing the per-module cost down to $12–$20.
Outdoor P10 DIP modules mlike P10/P16 beads, 6,000–8,000 nits, IP65 waterproof. It ranges from $30–$45 per module. Since DIP production is less common, there’s less price competition, so discounts for bulk orders are smaller . It is typically 5–10% for 500+ modules. The higher price is consistent across regions.
When scaling to full outdoor LED displays, the cost gap becomes even more pronounced. For example, a 10㎡ P10 display would cost $15,000–$25,000 with SMD, while $30,000–$45,000 with DIP. This is why most large outdoor projects now choose SMD.
Summary
Outdoor P10 DIP and SMD modules represent two generations of LED technology. DIP module is good for harsh outdoor environments. They offer higher brightness, omnidirectional light, inherent water resistance, and a longer lifespan. However, it comes with higher costs due to production and expensive lamp beads.
You can choose DIP only for specialized outdoor applications. for most projects, SMD have better value and performance.