When you choose or install LED display, we need to accurately calculate a range of parameters, such as the number of required power supplies and modules, wire diameter, and power distribution capacity. These calculations must be performed meticulously based on the specific size requirements of the project display.
Many professionals may not yet know these calculations. Today, Sight LED will explain these basic LED display calculation formulas.
Table of Contents
Toggle1.Determine LED Display Pixel Pitch Based on Viewing Distance and User Requirements
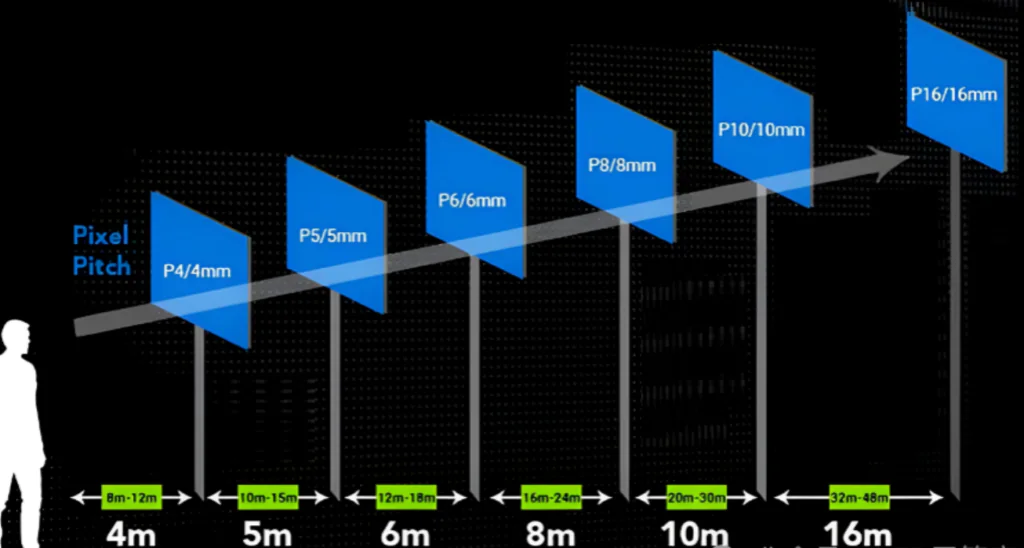
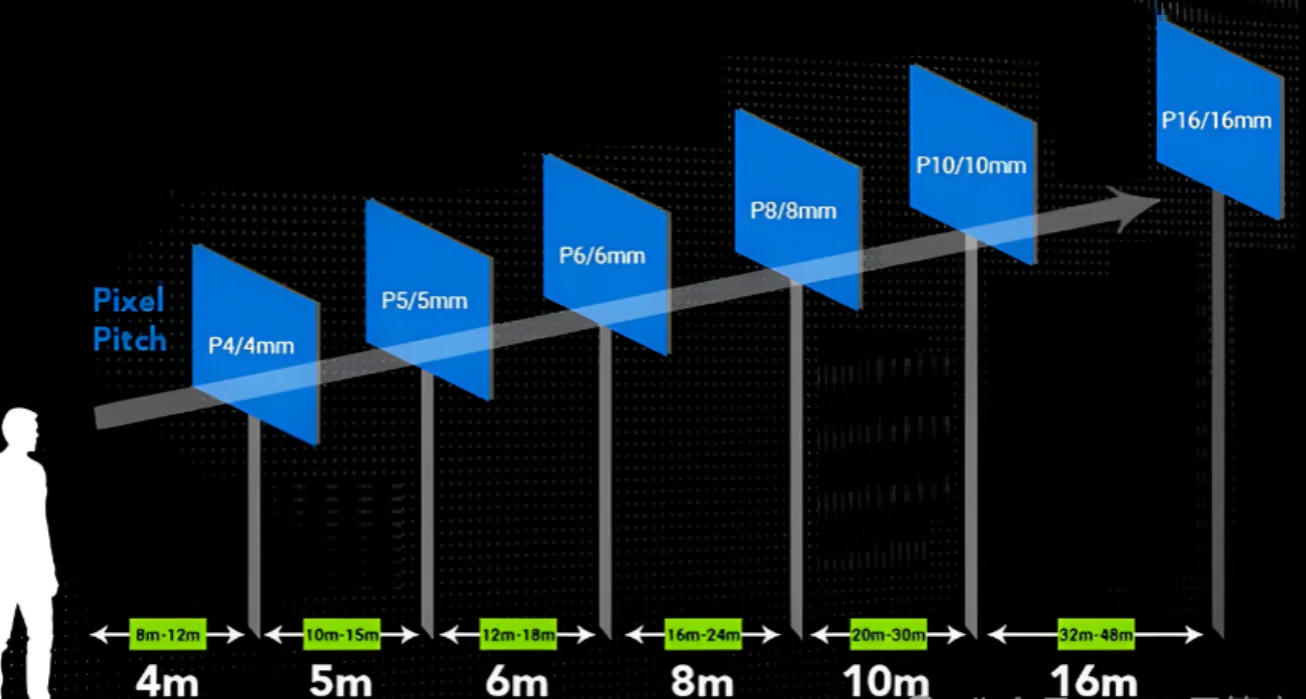
As a general guideline, We recommended viewing distance is 1000 to 3000 times the pixel pitch of the LED module.
Optimal viewing distance ≈ Pixel pitch (mm) × (1000–3000)
Minimum suitable viewing distance = Pixel pitch (mm) × 1000
Example
For a display with P1.5 :
Suitable viewing distance = 1.5 × 3000 = 4.5m
Minimum viewing distance = 1.5 × 1000 = 1.5m
2. Calculation Formula for LED Display Module Resolution
Horizontal pixel count of module (panel) = Horizontal dimension of module (panel) ÷ Pixel pitch
Vertical pixel count of module (panel) = Vertical dimension of module (panel) ÷ Pixel pitch
Example
For an indoor SMD P2 LED display:
Horizontal pixel count of P2 panel = 320 ÷ 2 = 160
Vertical pixel count of P2 panel = 160 ÷ 2 = 80
Thus, the module resolution of the P2 indoor LED display is 160×80.
3.Calculation Formula for the Number of Receiving Cards Required for LED Displays
We analyze two types of LED displays separately:
1) Displays Assembled with Panels (Modules)
Number of receiving cards for horizontal side = Number of horizontal modules of display ÷ Maximum horizontal module load per receiving card
Number of receiving cards for vertical side = Number of vertical modules of display ÷ Maximum vertical module load per receiving card
(2) Cabinet-Assembled LED Displays (One receiving card per cabinet)
Total number of receiving cards for cabinet display = Number of horizontal cabinets × Number of vertical cabinets
Example
For a P4 (80×40 resolution) display with 27 horizontal modules and 18 vertical modules, and the receiving cards with a load capacity of 256×512 pixels:
Number of receiving cards for horizontal side = 27 ÷ (256 ÷ 80) = 27 ÷ 3 = 9
Number of receiving cards for vertical side = 18 ÷ (512 ÷ 40) = 18 ÷ 12.8 ≈ 2
Total number of receiving cards for the entire display ≈ 9 × 2 = 18
4. Calculation of the Number of Processor Network Ports Required for LED Displays
A single network port can support a maximum of 650,000 pixels. To determine the required number of network ports for an LED display processor:
Number of required processor network ports = (Total number of modules × Panel resolution) ÷ 650,000
Example
For a 4.8m × 1.6m LED display using P2.5 modules (320×160mm dimension):
Total number of modules for the entire display ≈ (4800×1600) ÷ (320×160) = 150
Module resolution = (320 ÷ 2.5) × (160 ÷ 2.5) = 128 × 64 = 8192 pixels
Number of required network ports = (150 × 8192) ÷ 650,000 = 1.89 ≈ 2
Therefore, You need a processor with 2 network ports to drive this display.
5. Calculation Formula for LED Display Dimensions
Suppose we need to design approximately 100m² indoor P2.5 LED display. We usually adopt the 16:9 golden display ratio for calculation, using the following formulas:
Display length (A) = 4/3 × √Area
Display width (B) = 3/4 × √Area
Practical Calculation
Given A/B = 16/9 and A×B = 100m²:
Display length (A) = 4/3 × √100 ≈ 13.33m
Display width (B) = 3/4 × √100 ≈ 7.5m
6.Calculation of the Number of Modules Required for LED Displays
Number of horizontal modules (panels) = Display length ÷ Module length
Number of vertical modules (panels) = Display height ÷ Module width
Total number of modules (panels) = Total display area ÷ Module height ÷ Module width
Practical Calculation
For a P2.5 LED display with a length of approximately 13m and a height of approximately 9m:
Module length = 2.5 × 128 = 320mm = 0.32m
Module width = 2.5 × 64 = 160mm = 0.16m
Number of horizontal modules = 13 ÷ 0.32 = 40.625 ≈ 41
Number of vertical modules = 9 ÷ 0.16 = 56.25 ≈ 57
Total number of modules = 41 × 57 = 2337
7.Calculation of the Actual Total Area of LED Displays
Actual total display area = Total number of modules (panels) × Area of a single module (panel)
Example
For a P2.5 display with a length of approximately 12m and a height of approximately 9m:
Number of horizontal modules = 12 ÷ 0.32 = 37.5 ≈ 38
Number of vertical modules = 9 ÷ 0.16 = 56.25 ≈ 57
Actual total display area = (38 × 57) × (0.32 × 0.16) = 110.9m²
8. Calculation of LED Display Module Dimensions
Module (panel) length = Pixel pitch × Horizontal pixel count of module (panel)
Module (panel) width = Pixel pitch × Vertical pixel count of module (panel)
Example
For an indoor P2.5 product with 128×64 pixels:
P2.5 panel length = 2.5 × 128 = 320mm
P2.5 panel width = 2.5 × 64 = 160mm
Thus, the module dimensions of the indoor P2.5 LED screen are 320mm×160mm.
9. Calculation Formula for the Number of Power Supplies Required for LED Displays
The calculation is divided into two scenarios. They are displays assembled with frameless magnetic modules, and cabinet-assembled displays.
(1) Frameless LED Displays
Number of required power supplies = Total number of display modules ÷ Maximum module load per power supply
(2) Cabinet-Assembled LED Displays
Number of required power supplies = Total number of cabinets × (Number of modules per cabinet ÷ Maximum module load per power supply)
Example
For an LED display with 27 horizontal modules and 18 vertical modules, We can use a 4.2V 40A power supply. It can support 5–6 modules:
Total number of modules = 27 × 18 = 486
Number of required power supplies = 486 ÷ 6 = 81
10.Calculation Formula for the Number of Cabinets Required for LED Displays
Number of horizontal cabinets = Display length ÷ Single cabinet length
Number of vertical cabinets = Display height ÷ Single cabinet height
Total number of cabinets = Total display area ÷ Cabinet length ÷ Cabinet height
11.Calculation of Switching Power Supply Load Capacity and Power for LED Displays
Here is the information in an English table:
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Module Model | Q2AC20V3 |
| Input Voltage | 4.5V |
| Maximum Current | 5A |
| Unit Board Power | ≤22.5W |
| 40A Power Supply Load (number of unit boards) | 5-6 pieces |
| Maximum Power / ㎡ | ≤439W |
| Distribution Power / ㎡ | ≤663W |
| Average Power / ㎡ | ≤146W |
Key Notes for Switching Power Supply Load Calculation
To reduce the operating temperature of LED switching power supplies, improve stability and reliability, and extend service life, do not operate the power supply at full load. Generally, the load rate should be limited to 78% of the rated power when driving LED modules.
Common power parameters for LED displays include:
Maximum module (panel) power,
Maximum power per square meter,
Power distribution per square meter,
Average power per square meter.
Their definitions are as follows:
Panel power = Input voltage × Maximum current
Maximum power per m² = Panel power × Number of modules per m²
Power distribution per m² = Maximum power per m² ÷ 78% ÷ 85%
Average power per m² = 1/3 × Maximum power per m²
12. Calculation for Selecting Main Cables of LED Displays
Here is the information in an English table:
| Wire Specification (mm²) | Safe Carrying Capacity (A) | Maximum Carrying Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0~8 | 1.8 |
| 1.5 | 8~12 | 2.6 |
| 2.5 | 12~20 | 4.4 |
| 4 | 20~25 | 5.5 |
| 6 | 25~32 | 7.0 |
| 10 | 32~50 | 11.0 |
| 16 | 50~65 | 14.3 |
| 25 | 65~85 | 18.7 |
| 35 | 85~115 | 25.3 |
| 50 | 115~150 | 33.0 |
| 70 | 150~175 | 38.5 |
| 95 | 175~225 | 49.5 |
| 120 | 225~250 | 55.0 |
| 150 | 250~275 | 60.5 |
| 185 | 275~350 | 77.0 |
| 240 | 350~400 | 88.0 |
The selection of main cables for LED displays is based on the power distribution per square meter of the panel.
First, we can calculate the total display power distribution, then derive the total distribution current using the power formula.
If the total current exceeds 30A, we need three-phase power supply, with each phase bearing 1/3 of the total current.
Finally, we should confirm the cable diameter by referring to the cable ampacity table.
Relevant Specifications
According to the Code for Design of Power Supply and Distribution Systems and Code for Electrical Design of Civil Buildings.
For 220V lighting loads supplied by the regional public low-voltage power grid, single-phase 220V power supply is allowed if the line current does not exceed 30A; otherwise, three-phase four-wire 220/380V power supply shall be adopted.
Calculation Steps
Total display power distribution = Power distribution per m² × Total display area
Total current = Total display power distribution ÷ 220V
If total current > 30A, use three-phase power supply
Single-phase current = Total current ÷ 3
Determine the cable diameter by matching the single-phase current with the cable ampacity table
Practical Calculation 1
For an indoor P2.5 display with a panel power of 23W and a total area of 20.48m²:
P2.5 module dimensions: 320×160mm
Number of modules per m² = 1 ÷ 0.32 ÷ 0.16 ≈ 20
Maximum power per m² = 20 × 23W = 460W
Power distribution per m² = 460W ÷ 78% ÷ 85% = 694W
Total display power distribution = 694W × 20.48 = 14,213W
Total distribution current = 14,213W ÷ 220V = 65A
Since 65A > 30A, three-phase power supply is adopted
Single-phase current = 65A ÷ 3 = 21.6A
Referring to the cable ampacity table, we can select a 4mm² cable
Practical Calculation 2
For an P8 outdoor LED display with 1,500 panels and a maximum panel power of 28W:
Total maximum display power = 1,500 × 28W = 42,000W
Total display power distribution = 42,000W ÷ 78% ÷ 85% = 63,349W
Total distribution current = 63,349W ÷ 220V ≈ 288A
Since 288A > 30A, three-phase power supply is adopted
Single-phase current = 288A ÷ 3 = 96A
Referring to the cable ampacity table, we can select a 35mm² cable
Conclusion:
We have guide you the above basic calculation formulas and case studies. They are commonly used in the design and installation of LED displays. We hope this guide are helpful for you all. If you need to select an LED display screen, please feel free to contact us.